A Simple Note for k-means clustering
1. What is k-means clustering
In short, K-means is an unsupervised clustering algorithm for partitioning a d-dimensional population into k sets. Formally, given a set of observations X=(x1,x2,...,xn),xi∈Rd,i=1,2,...,n, each observation is a d-dimensional vector, k-means
-
initializes k centroids denoted as C={c1,c2,...ck} to represent k clusters, denoted as S={S1,S2,...,Sk}
-
in each step t≥1,
2.1 for each xi, finds the first nearest centroid, denoted as c∗t,i=argminct,j‖
2.2 expectation step: adds x_i into the cluster represented by c^*_{t, i}, S updated
2.3 maximization step: assigns c_{t+1, j} = \frac{1}{ \vert S_{t, j} \vert } \sum_\limits{x_i \in S_{t, j}} x_i, j=1, 2, ..., k, C updated.
-
iterate step t until converged or reach the max iterate number
The objective is to minimize the within-cluster sum of squares(WCSS),
\begin{equation} \underset{C}{\operatorname{argmin}} \sum_{j=1}^k \sum_{x \in S_j} {\| x - c_j \|}^{2} \end{equation}which is an NP-hard problem. Kmeans does not guarantee convergence to the global optimum.
2. Initialization
Centroids initialization plays an important part in kmeans. The result may rely on the initial centroids badly. One simply method is to run kmeans multiple times. There are several initialization methods. The commonly used methods are Forgy random, random partition and k-means++.
-
Forgy random uniformly randomly selects k instances from the population as centroids.
-
Random partition randomly partition the population into k clusters.
-
K-means++ weights the probability for a data point to be chosen as center according to it’s distance from the closest already chosen centers, unlike uniformly random.
2.1 k-means++
-
find first center: uniformly randomly choose an instance as center from X, denoted as c_1, makes the already chosen centers as C=\{c_1\}
-
find the next k-1 centers: repeat the below steps k-1 times
2.1 for each instance x_i, find the first nearest center, denoted as c_i, c_i \in C
2.2 calculates the square of the distance between x_i and c_i, denoted as d_{i}^2 = \| x_i - c_i \|^2
2.3 calculates the probability density function as P(x_i) = {d_i^2}/{\sum_\limits{i=1}^n{d_i^2}}
2.4 chooses center randomly with the above pdf, denoted as c_{next}, updates C= C + \{c_{next}\}
3. A numpy python implementation
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. create samples
X, y = make_blobs()
# 2. centroids initialization
def _cal_min_distances(X, centers):
distances = np.sum(np.square(X[:, np.newaxis, :] - centers), axis=2)
min_distances = np.min(distances, axis=1)
return min_distances
def _Lloyd_centroids_init(X, k):
N = X.shape[0]
idx = np.random.choice(N, size=k, replace=False)
return X[idx]
def _kmeans_plus_plus(X, k):
N = X.shape[0]
first_center = X[np.random.choice(N)]
centers = [first_center]
for i in range(k-1):
distances_min = _cal_min_distances(X, np.array(centers))
pdf = distances_min/np.sum(distances_min)
# with pdf like this,
# the already chosen instances will be excluded, and
# the instances far away from centers will have higher probablities to be chosen
new_center_idx = np.random.choice(N, p=pdf)
new_center = X[new_center_idx]
centers.append(new_center)
return centers
def centroids_init(X, k, method):
# defalut method 'kmeans++'
if method == 'random':
return _Lloyd_centroids_init(X, k)
return _kmeans_plus_plus(X, k)
# 3. utils functions
def _find_first_nearest_centroid(X, centroids):
distances = np.sum(np.square(X[:, np.newaxis, :] - centroids), axis=2)
first_nearest_centroid_idx = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
return first_nearest_centroid_idx
def _ndarray(arrs):
return np.array(arrs, dtype=object)
# 4. kmeans
def kmeans(X, k, method, max_iter=100):
centroids = centroids_init(X, k, method)
iterate_left = max_iter
while iterate_left > 0:
centroid_idx = _find_first_nearest_centroid(X, centroids)
clusters = [X[centroid_idx==i] for i in range(k)]
new_centroids = [np.mean(clusters[i], axis=0) for i in range(k)]
if np.allclose(centroids, new_centroids):
print('converage at step', max_iter-iterate_left)
return _ndarray(clusters), _ndarray(new_centroids), centroid_idx
else:
centroids = new_centroids
iterate_left -= 1
return _ndarray(clusters), _ndarray(new_centroids), centroid_idx
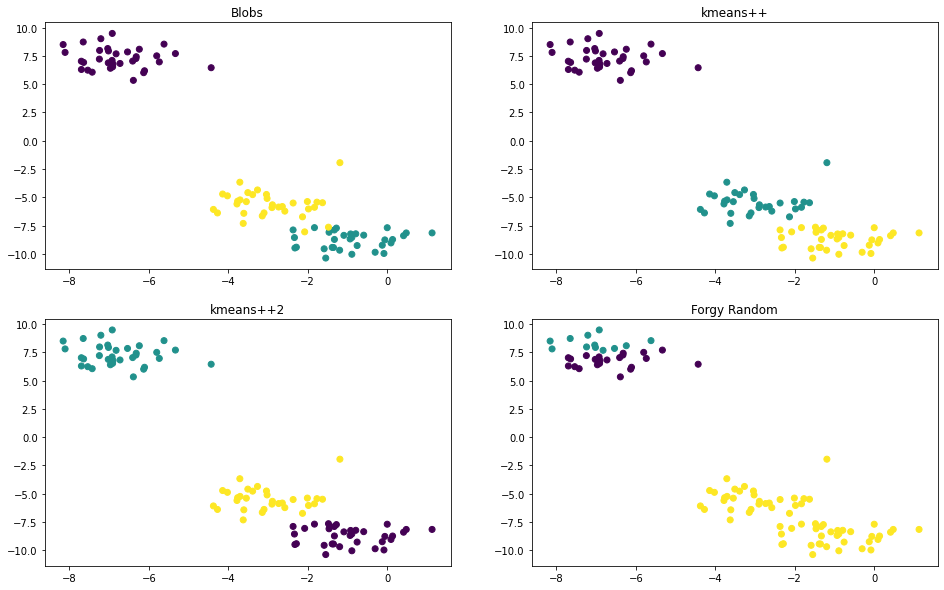
# 5. result and demonstration
clusters_plus_plus, centroids_plus_plus, labels_plus_plus = kmeans(X, 3, 'kmeans++', 100)
clusters_plus_plus2, centroids_plus_plus2, labels_plus_plus2 = kmeans(X, 3, 'kmeans++', 100)
clusters_plus_forgy, centroids_forgy, labels_forgy = kmeans(X, 3, 'random', 100)
# plot
def plot_scatter(ax, X, labels, title):
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=labels)
ax.set_title(title)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(16, 10))
plot_scatter(axes[0, 0], X, y, 'Blobs')
plot_scatter(axes[0, 1], X, labels_plus_plus, 'kmeans++')
plot_scatter(axes[1, 0], X, labels_plus_plus2, 'kmeans++2')
plot_scatter(axes[1, 1], X, labels_forgy, 'Forgy Random')
#